










Project Target
0% Remaining
50,000
Trees Planted out of 50,000 Trees
Project Location:
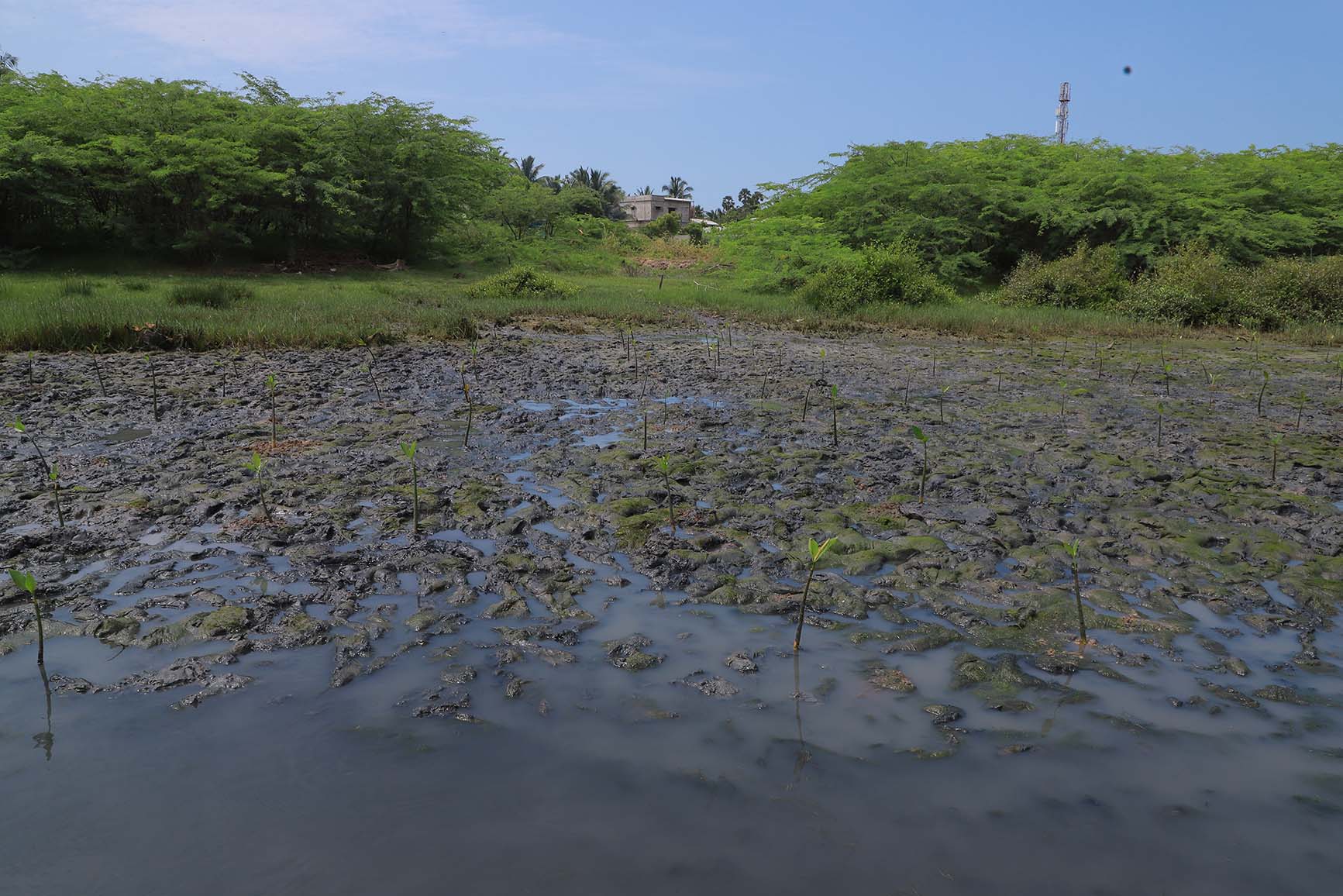
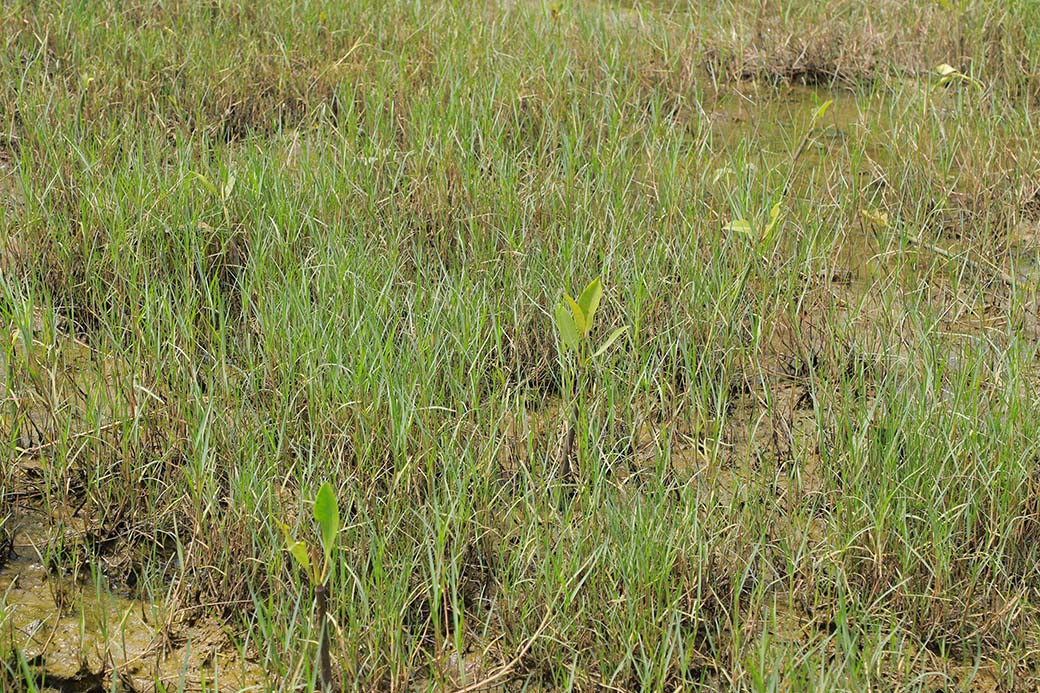
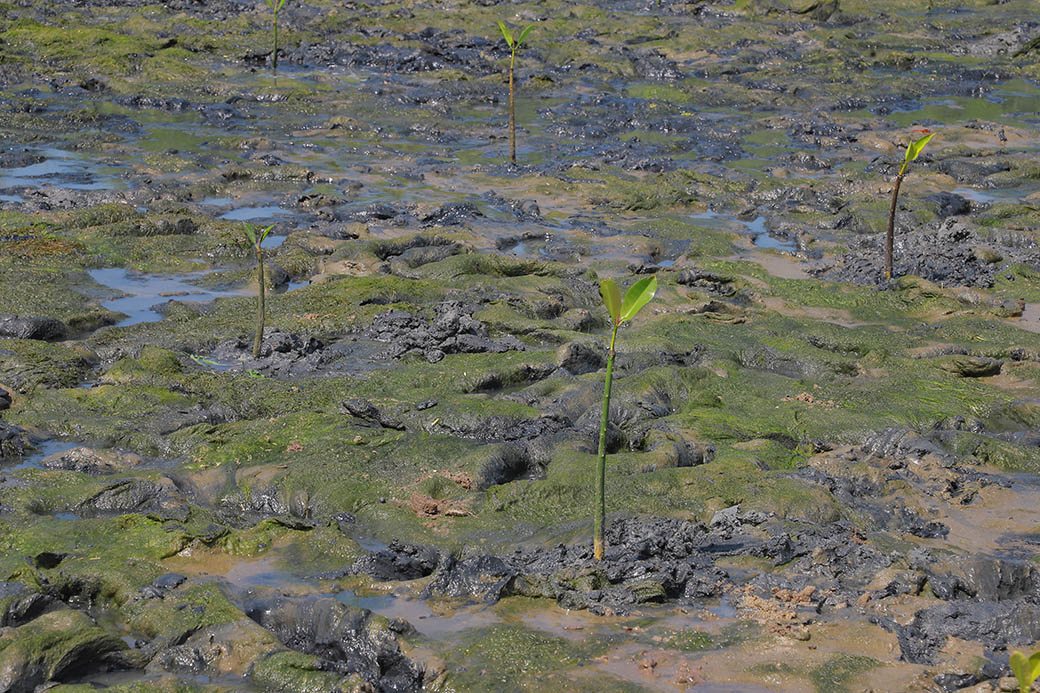
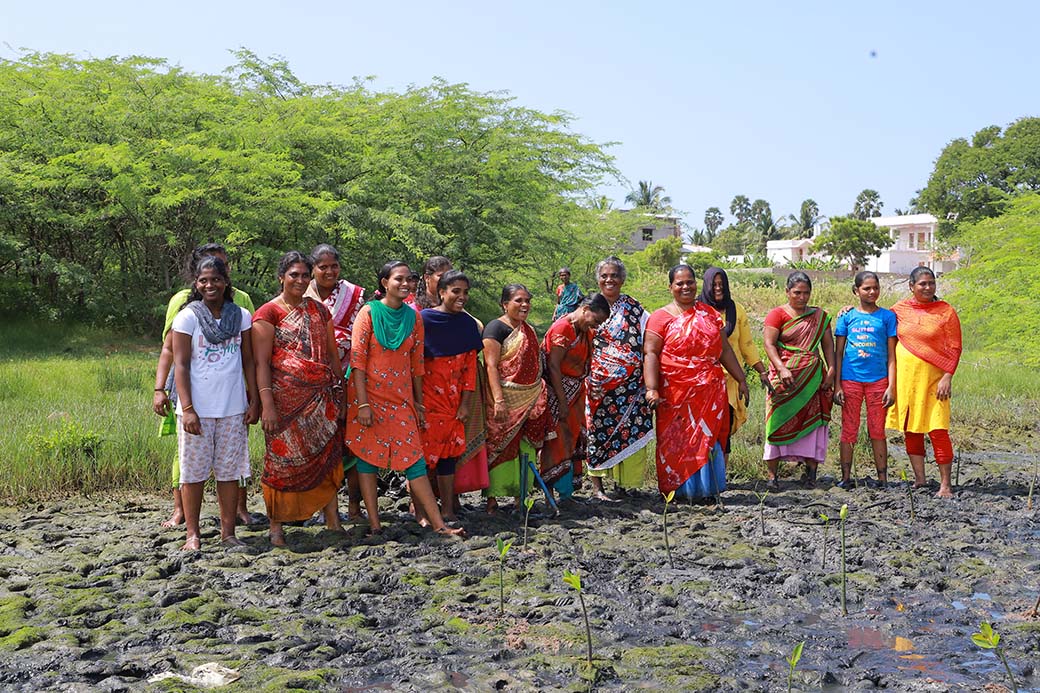
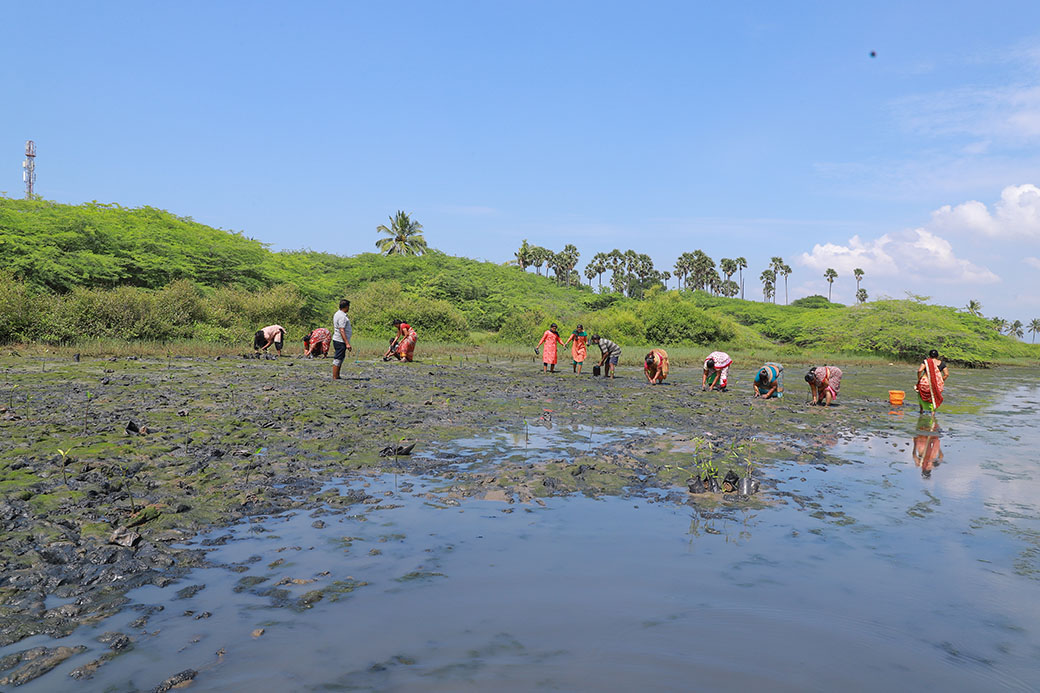
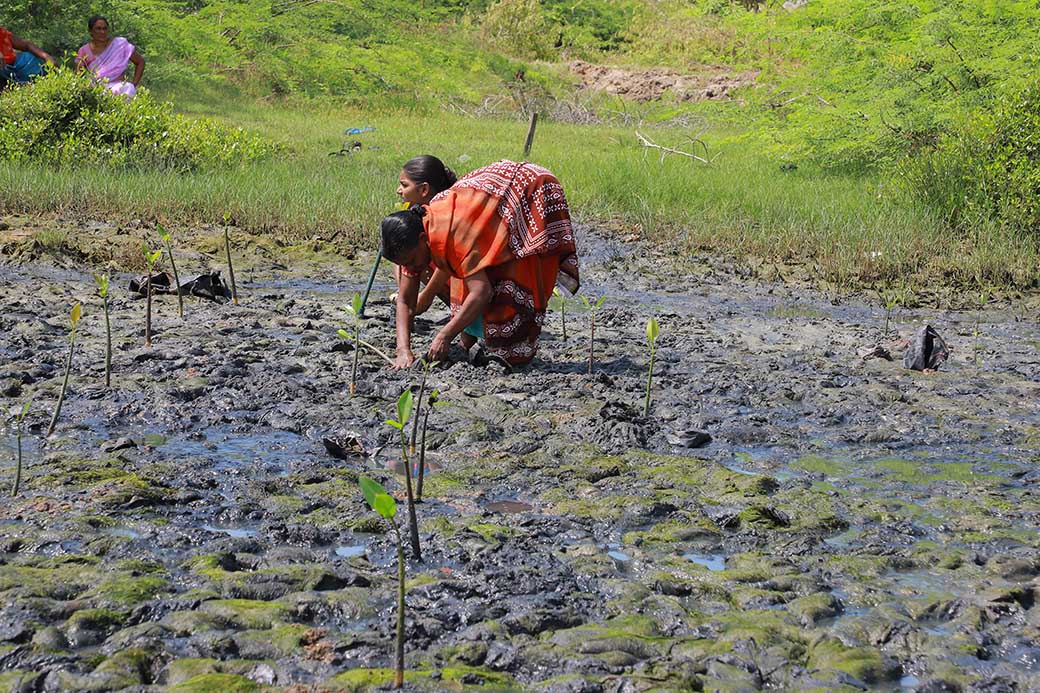
The project involves plantation of trees on estuary land owned by the Rajakkamangalam Panchayat in Rajakkamangalam village, Kanyakumari District of Tamil Nadu. The estuary has a wetland of 200 hectares which holds brackish water due to the mixing of freshwater from Pandiyar and the seawater from high tide.
Project Aim
“After the occurrence of tsunami in Tamil Nadu, India, frequent happenings of forcible intrusion and withdrawal of sea water with maximum threatening level affect the psychology of coastal communities and hence, consequential needs have arisen on programmes of disaster preparedness and risk management, livelihoods of people and conservation works. Mangrove trees, which serve as the savior of coastal eco system from intensive tidal waves, are found growing luxuriantly in the inter-tidal regions along the estuaries, backwater, islands and other protected areas. However, this valuable plantation has been deforested to such an extent that the eco system along the west coast of India is found under degraded condition.”, stated the SEEDS Trust in an article. Mangroves form the most important and unique feature of this area with their ability to thrive in both dry as well as flood-like conditions. Due to the presence of saltwater and freshwater at the same time, both types of plants are present and support the habitat in their own unique way.
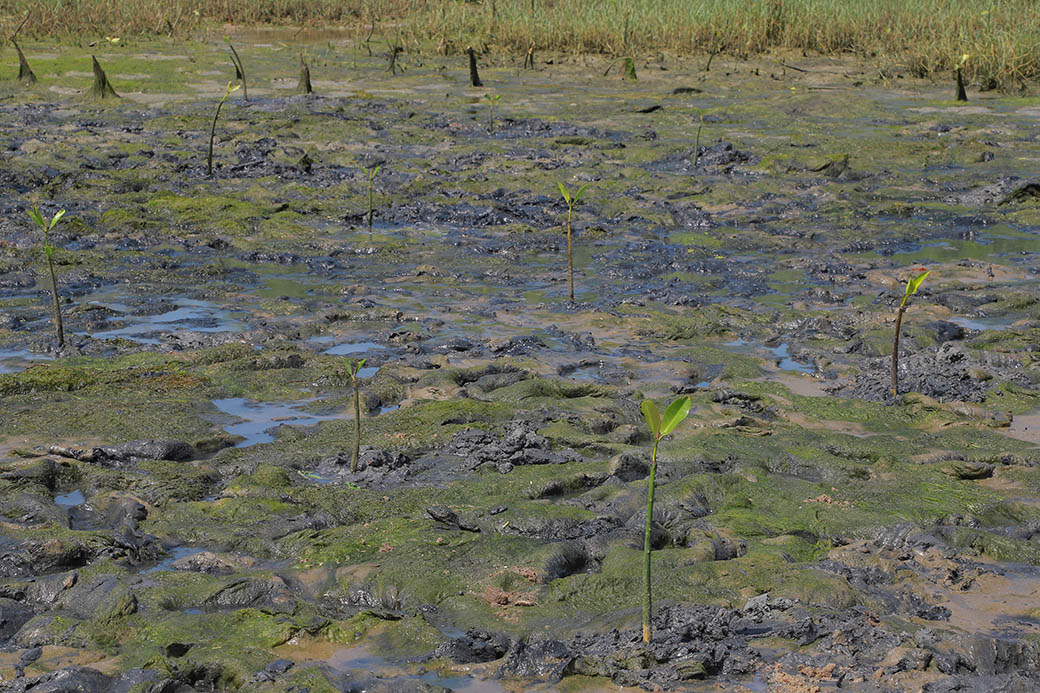
Studies have found that land loss due to rising sea levels and erosion is causing the displacement of rural communities (entire villages in some cases) and exacerbating poverty. The planting site was once a designated mangrove forest, with a diverse species of mangroves and other associated species. However, due to the land conversion for salt pans, the estuary degraded and is now either deforested or occupied by several invasive species. Climate change, sea level rise, and sediment starvation have contributed to land loss in the region and, thus, loss of forest cover. Scientific studies also talk about the role of mangroves in food security, containing the effect of storm surges and tsunamis, creating livelihood opportunities, CO2 sequestration, sediment trapping, nutrient recycling, etc.
The Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO) of the United States emphasizes the importance of mangroves in the food web of coastal ecosystems, therefore, making a direct impact on the terrestrial and aquatic life of the area. Mangrove Society of India's Executive Secretary Dr Arvind Untawale, mentions the significance of mangroves against tsunamis, pollution, protecting marine biodiversity and producing medicinal products.
Rhizophora mucronata, Rhizophora apiculata, Rhizophora racemosa, Avicennia alba, Avicennia bicolor, Avicennia officinalis, Avicennia marina, Bruguiera parviflora, Bruguiera gymnorrhiza, Excoecaria agallocha, Ceriops tagal, Acanthus ilicifolius, Calophyllum inophyllum, Azadirachta indica, Pongamia pinnata, Thespesia populnea, Mangifera indica, Artocarpus heterophyllus, and Borassus flabellifer
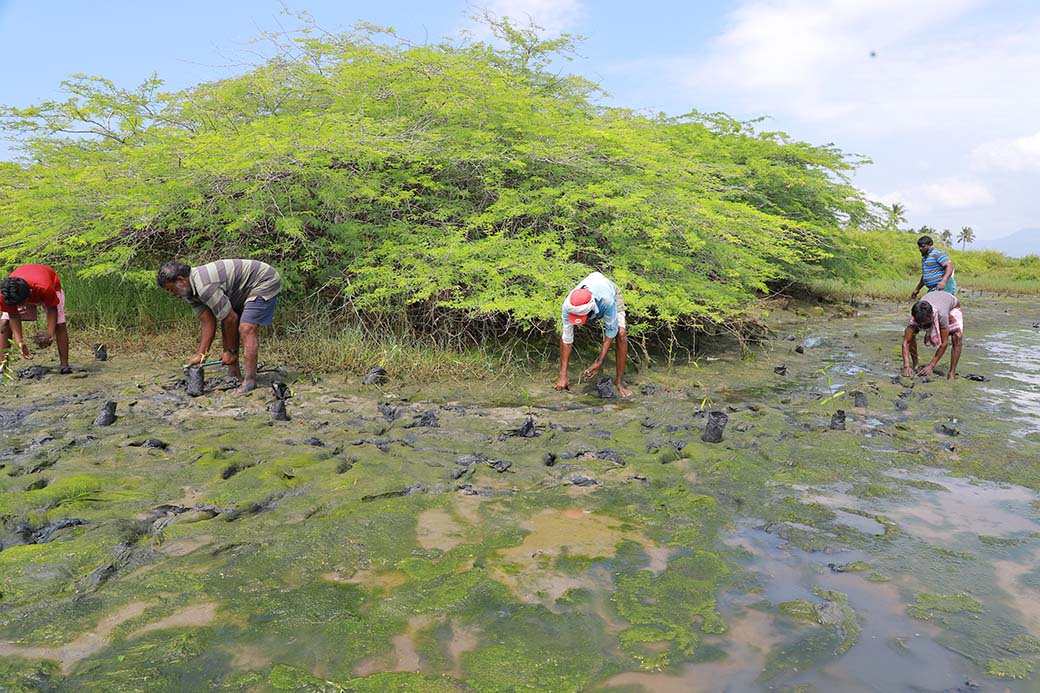
The plantation of mangroves will directly impact rural livelihoods by creating jobs in nursery and planting activities, improving fisheries catch, providing flowers, fruit, fodder and fuel to rural communities and wildlife. The plantation will enhance the environment by generating oxygen and reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, not only to fight climate change but also to benefit the endemic wildlife. Further, reforestation will provide ample livelihood opportunities for the people in the buffer area, preventing them from venturing into the forest and minimizing chances of conflict and empowerment of the dwellers as a result. The valued mangrove species will also improve the habitat for breeding of small fish, crabs and prawns which have high economic values even in the local markets. Mangrove forests aid as soil binder and will, thus, reduce soil erosion, strengthen embankment and significantly arrest tidal and cyclonic waves.
| Name of the Company | Number of Trees Planted | Fiscal Year |
|---|---|---|
| HDB Financial Services | 25,000 | 2020-21 |
| DCB Bank | 25,000 | 2020-21 |
Social Impact of Growing Trees
Community Engagement
Tree planting initiatives often involve local communities, which can lead to greater community cohesion.
Ecological Education
Provides opportunities for community members, especially children, about the importance of environmental sustainability.
Urban Beautification
Trees contribute to the aesthetic enhancement of urban areas, making cities more pleasant and liveable.
Climate Resilience
By improving green cover, tree planting helps make communities more resilient against climate impacts like heatwaves.
Employment Creation
Planting trees creates employment for local community members like planting and maintenance, administrative roles, and more long-term jobs in management.
Wildlife Habitat
Trees provide critical habitats for various species of wildlife. Enhancing tree cover helps preserve biodiversity, which can be an ecological boon for local communities
Copyrights @ 2025 All rights reserved by Pangea EcoNetAssets Pvt Ltd.